New to wholesale?
We’ve created a wholesale jargon buster to help learn the wholesale lingo.
Let’s start with ‘what is wholesale?’
Wholesale is the business of selling goods in large quantities and at low prices, typically to be sold on by retailers at a profit.
For example, a wholesaler will invest in buying bulk, usually by the truckload from a manufacturer/supplier at a discounted price obtained by purchasing economies of scale. Wholesalers pass on the savings to retailers that purchase in smaller quantities at a higher unit cost to sell to the consumer/ end user.
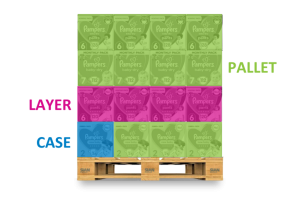
In wholesale, there are three main buying quantities; case, layer and pallet.
Starting with the smallest, a Case (Blue) is a collection of units or pcs. Next up is a layer. A Layer (Pink) is the number of cases that fit horizontally on a pallet. And finally, the Pallet (Green) quantity metric signifies how many cases stack onto a pallet.
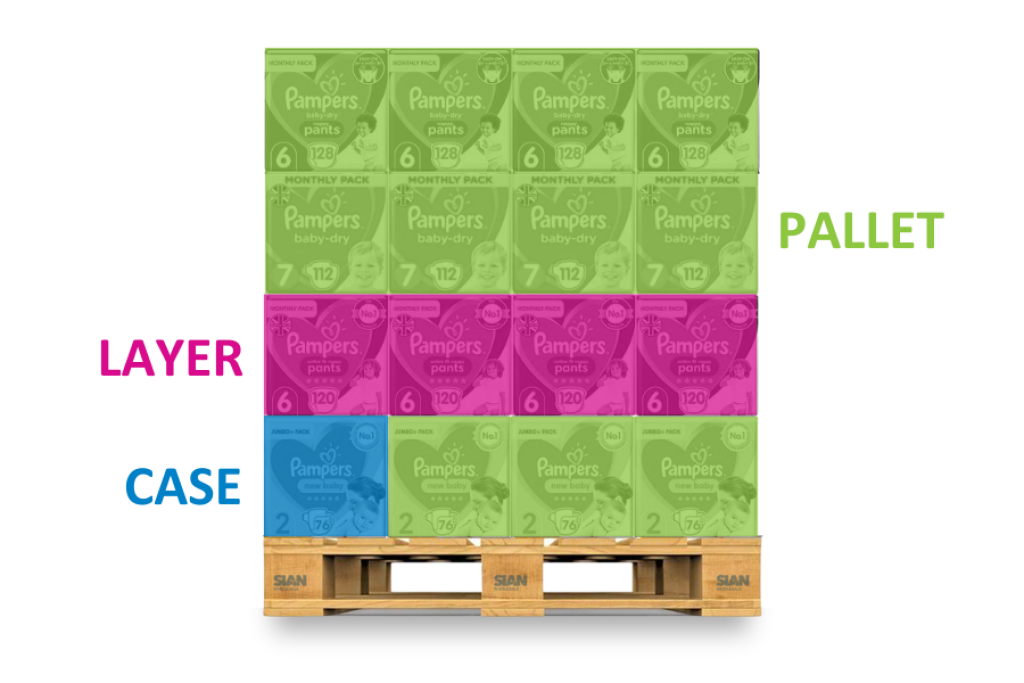
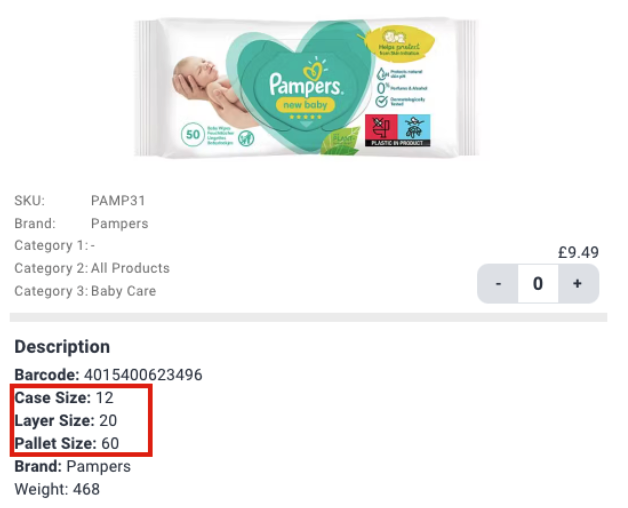
We show all three quantities on our stocklist. If we take a look at the image below of our CSV stocklist.
It indicates there are 12 units/pcs of Pampers Baby Wipes 50s Sensitive New Baby in a Case, in other words, there are 12 packs of 50 wipes. A layer in this example contains 20 Cases, and a Pallet is made from 60 stacked cases. The prices shown are for the Case quantity.
The SIAN Store
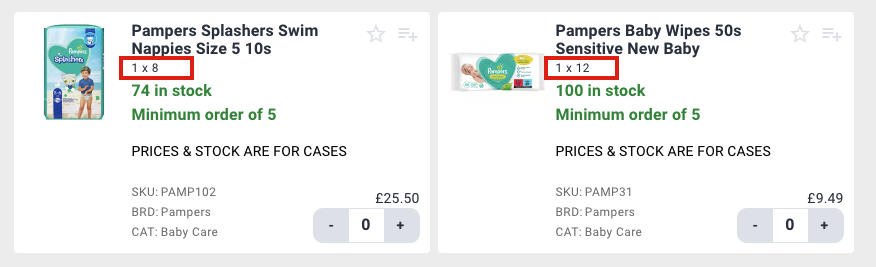
The same information is available on the SIAN online store. Case quantities on the SIAN store are shown as 1 (case) x 12 (units).
On the *category page level, click through the **product page level to see the layer and pallet information.
*Store category Level
**Store Product Level
Minimum Order Value (MOV)
Suppliers use Minimum Order Value (MOV) or Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) to ensure the order size is large enough to be profitable. SIAN’s MOV is a strict £5000 with a MOQ of 5 cases per SKU. Due to shipping costs, we recommend different MOV per region. View the full MOV regional breakdown here.
Please note we DO NOT offer smaller test orders.
SKU
A stock-keeping unit, or SKU, is a unique code assigned to every type of item that a wholesaler sells. SKUs are an important part of the merchandising structure allowing sellers to arrange and organise their inventory according to the product’s SKU.
Unit Barcodes
Barcodes are also used to identify products. Unlike SKUs that are usually unique to individual products, barcodes are used universally and remain constant for a product no matter what quantities the retailer sells it in.
EAN & UPCs
Other types of barcodes are EAN (European Article Number) or a UPC (Universal Product Code). The difference being the UPC format is 12 digits while the EAN is 13. These two formats are predominantly used in their own regions. UPC is used only in the US and Canada, while the EAN is used globally.
Just to confuse matters further, products also have an outer barcode. The outer barcode is found on the product case/ carton. These barcodes are larger than the standard EAN or UPCs found on the product, making them easier to see in a warehouse environment.

The outer barcodes and inner barcodes are scanned in the booking-in process. Booking-in process monitors the flow of stock entering the warehouse. By scanning the products, the goods-in team log the product’s details onto the system and update the stock levels.
Scanning Outer Barcode
These details then populate the stocklist and product listings on the online store. We also use this time to assess for any damages that may have occurred during transport and remove any damaged items to keep our stock to the highest quality.
Bin Location
After the stock is booked, the warehouse team transports it to its allocated Bin Location.
A bin location is a designated inventory storage location; this can be a shelf, a pallet location, a storage area, or any other place where products are stored (ideally not in the aisles). Good bin location management is essential for warehouse housekeeping and for an efficient workflow structure.
Putting a pallet in a Bin Location
Bin locations are used on the pick, the process of pulling inventory for an order and preparing them for shipping.
Picking a mixed pallet
Pallet Wrap
Pallet wrap is spun around the product cases and layers to secure the goods for transport. To further protect areas susceptible to damage, such as the corners, dense cardboard edge guards are added between layers of pallet wrap.
Wrapping a pallet with corner protection
Shipping
Depending of the size of the order, different methods are used to transport goods.
While smaller orders will fit in most forms of transport and can be combined with other orders to make for effective freight costs, conversely, larger orders will require full trucks or containers.
Containers
There are two standard shipping container sizes, 20ft and 40ft.
Freight forwarder
Freight forwarders act as an intermediary between the company that makes the shipment and the final destination for the goods.
Our operations use our trusted freight forwarders network to arrange transport options such as sea/ocean freight, rail freight, road transport and air freight shipment.
Tail-lift
A tail lift is a mechanically-operated platform mounted to the end of a vehicle to aid with loading and unloading freight. Because the tail lift can be conveniently lowered or raised, it is used as an alternative for times when a forklift is not available or suitable.
Please specify with your account manager if you require delivery with a tail lift.
Example of a tail lift lorry/truck
Net payment terms
Net payment plans offer flexibility to the buyer to pay for items after they have had time to sell the items you supplied. For instance, a buyer may request invoice payment terms of 30, 60 or 90 days. This is usually referred to as net 30, net 60 or net 90, etc.
Invoice
The document a seller sends to a retailer once the retailer has confirmed a submitted order. The invoice includes information about the amount of goods sold, what those goods are, the individual cost of the products, additional charges (such as shipping fees, etc.), and contact information for both parties.
Proforma invoice
A proforma invoice is a preliminary bill or estimated invoice which is used to request payment from the committed buyer for goods or services before they are supplied. A proforma invoice includes a description of the goods, the total payable amount and other details about the transaction.
Manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP)
The price you recommend your retailer charge for your items. The term is used interchangeably with “Recommended Retail Price” (RRP).
Lead time
Also known as turnaround time. The amount of time it takes (usually days) from the moment an order is placed until the order is shipped from a wholesale seller to a retailer.
POR (Profit on return)
Profit on return is calculated by subtracting a unit’s selling price from the cost price, dividing that difference by the selling price, and multiplying that number by 100. Or use the POR calculator on the SIAN store.
Back-order
Products that have been ordered but have not shipped typically due to a manufacturer’s lack of inventory.
… And that’s it, you made it to the end of the article! These are some of the most commonly used words/terms in the wholesale industry. This article will evolve over time as we add more words/ terms that appear in our FAQs.
If you have any questions or want to know more about how SIAN Wholesale operates, please contact [email protected].